Explore our extensive collection of informative charts and graphs dedicated to drill bit statistics, a vital resource for professionals in construction, woodworking, and metalworking industries. Our visually engaging diagrams provide a deep dive into drill bit sizes, materials, and usage trends, offering valuable insights for making informed decisions. Whether you’re comparing the durability of carbide and high-speed steel drill bits, analyzing market preferences, or assessing the cost-effectiveness of various sizes, our data-driven approach ensures you have the latest and most relevant information at your fingertips. Perfect for both industry veterans and newcomers, our charts and graphs are designed to enhance understanding and drive efficiency in your projects.
Drill Bit Sizes Distribution Chart
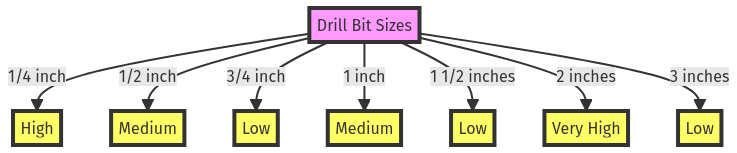
This chart illustrates the range of drill bit sizes, such as 1/4 inch, 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch, and so on, along with their respective popularity or usage frequency in various industries, categorized as high, medium, low, or very high.
| Drill Bit Size Range | Common Uses | Popularity/Usage Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1/16-inch to 1/4-inch | Basic home projects, fine woodworking | Very High (most popular for DIY) |
| 1/4-inch to 1/2-inch | Versatile for a range of DIY and professional tasks | High (widely used) |
| Over 1/2-inch | Specialized industrial or construction tasks | Moderate (more niche applications) |
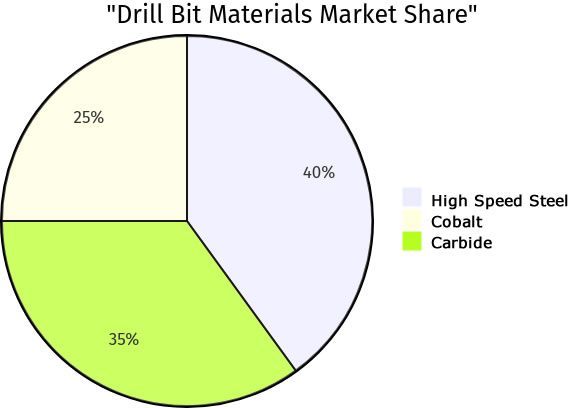
| Material | Characteristics | Common Uses | Market Share/Usage Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | Versatile, affordable | General-purpose drilling | Dominant in general use |
| Cobalt | Heat resistant, durable | Drilling hard metals like stainless steel | Common in professional use |
| Carbide (Tungsten Carbide) | Extremely hard, heat resistant | Specialized industrial applications | Prevalent in industrial settings |
This is a pie chart displaying the different materials used in drill bit manufacturing (e.g., high-speed steel, cobalt, carbide) and their market share or usage rate.
Durability or Lifespan
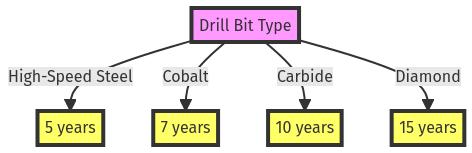
This chart shows the average lifespan of different types of drill bits under normal usage conditions.
| Drill Bit Type | Material Used For | Average Lifespan | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | Metal, Wood | Several hundred holes | Lifespan can vary based on the material and usage conditions. |
| Cobalt | Harder Metals | Longer than HSS | Durable and heat resistant, ideal for tough materials. |
| Carbide-Tipped | Various | Thousands of holes | Extremely durable, often used in industrial settings. |
| Masonry | Concrete, Stone | Hundreds of holes | Shorter lifespan due to material abrasiveness. |
[/vc_column_text]
Drill Bit Price Range Table
This chart shows the average price range of the different types of drill bits.
| Material Type | Size Range | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | 1/16″ – 1/4″ | $1 – $10 |
| 5/16″ – 1/2″ | $5 – $20 | |
| 5/8″ – 1″ | $10 – $30 | |
| Cobalt | 1/16″ – 1/4″ | $5 – $15 |
| 5/16″ – 1/2″ | $10 – $30 | |
| 5/8″ – 1″ | $20 – $50 | |
| Carbide | 1/16″ – 1/4″ | $10 – $30 |
| 5/16″ – 1/2″ | $20 – $60 | |
| 5/8″ – 1″ | $30 – $100+ | |
| Diamond | 1/16″ – 1/4″ | $20 – $60 |
| 5/16″ – 1/2″ | $30 – $100+ | |
| 5/8″ – 1″ | $50 – $200+ | |
| Titanium Coated | 1/16″ – 1/4″ | $5 – $20 |
| 5/16″ – 1/2″ | $10 – $25 | |
| 5/8″ – 1″ | $15 – $40 |
Cost-Effectiveness Insights
- HSS Drill Bits: Generally the most cost-effective for general use, especially in softer materials like wood and plastic.
- Cobalt Drill Bits: More expensive but offer better performance and durability, especially in harder materials like stainless steel.
- Carbide Drill Bits: High price but extremely durable and efficient for specialized industrial applications, particularly in hard materials.
- Diamond Drill Bits: The most expensive, used for very specific applications like glass, stone, or very hard metals.
- Titanium Coated Bits: Offer a balance between durability and cost, suitable for heavier-duty tasks than standard HSS bits without the high cost of cobalt or carbide.
Drill Bit Usage in Different Industries
This table provides a concise overview of the typical preferences and uses of drill bits in various industries, highlighting the diversity in material choice and application based on industry-specific requirements.
| Industry | Preferred Materials | Purpose | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | HSS, Cobalt, Carbide-tipped | Drilling wood, metal, concrete | Durability, versatility, masonry bits for concrete |
| Woodworking | HSS, Carbon Steel, Titanium | Drilling in wood and composites | Brad-point for precision, spade and Forstner bits |
| Metalworking | HSS, Cobalt, Carbide | Drilling in metals like steel, aluminum | High durability, heat resistance |
| Automotive | HSS, Cobalt, Titanium-coated | Drilling in metals and alloys | Heat resistance, used in drills and presses |
| Electronics/Precision | HSS (specialized coatings) | Drilling in delicate materials | Micro drill bits for precision |
| Masonry/Stonework | Carbide-tipped | Drilling stone, concrete, brick | Hard tips, used with hammer drills |
| Plumbing and HVAC | HSS, Cobalt, Step Drill Bits | Drilling pipes, sheet metal | Step bits for variable sizes, durability |
| Aerospace | HSS, Cobalt, Carbide, Diamond | Drilling in alloys, composites | Precision, heat resistance, controlled environments |
Drill Bit Types and Their Efficiency in Different Materials
The drilling speed and efficiency of drill bits can vary significantly based on their type and the material they are designed to cut into. Below is a table that outlines common types of drill bits and their general performance in terms of speed and efficiency across different materials:
| Drill Bit Type | Efficiency in Wood | Efficiency in Metal | Efficiency in Masonry | Efficiency in Plastic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Twist Drill Bits | Good | Excellent | Poor | Good |
| Brad-Point Bits | Excellent | Poor | Not Suitable | Good |
| Spade Bits | Excellent | Poor | Not Suitable | Fair |
| Auger Bits | Excellent | Poor | Not Suitable | Fair |
| Forstner Bits | Excellent | Poor | Not Suitable | Fair |
| Hole Saw | Good | Good | Not Suitable | Good |
| Masonry Bits | Poor | Poor | Excellent | Poor |
| Cobalt Drill Bits | Good | Excellent | Poor | Good |
| Carbide Drill Bits | Fair | Excellent | Excellent | Fair |
| Step Drill Bits | Fair | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Diamond Drill Bits | Poor | Fair | Excellent | Poor |
Key Insights:
- Twist Drill Bits: Versatile and efficient in metal, also suitable for wood and plastic.
- Brad-Point Bits: Ideal for precise drilling in wood, not suitable for metal or masonry.
- Spade and Auger Bits: Excellent for fast drilling in wood, not recommended for other materials.
- Forstner Bits: Best for flat-bottomed holes in wood, not for metal or masonry.
- Hole Saws: Good for making large diameter holes in various materials, but not suitable for masonry.
- Masonry Bits: Specifically designed for concrete, brick, and stone, not efficient in wood or metal.
- Cobalt Drill Bits: Excellent in metal, particularly hard metals, and usable in wood and plastic.
- Carbide Drill Bits: Very hard, excellent for metal and masonry, but can be brittle in wood.
- Step Drill Bits: Ideal for drilling through thin metals and plastic, offering multiple sizes in one bit.
- Diamond Drill Bits: Used for very hard materials like glass and tile, not efficient for wood or metal.
The table above provides a general guide, but the actual performance can vary based on the quality of the drill bit, the specific material being drilled, and the drill’s power and speed settings.
Factors Influencing Drill Bit Sales Distribution
This table is a simplified representation and should be used as a guideline to understand potential market dynamics. The actual sales and popularity would require specific market research data. The categories like ‘High’, ‘Moderate’, ‘Strong’, etc., are relative and could vary over time and with changing market conditions.
| Region/Country | Industrial Development | Local Resources | Construction Trends | DIY Culture | Technological Advancements | Regulatory Environment | Economic Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | High | Diverse | High | Strong | High | Moderate to Strict | Wealthy |
| China | High | Diverse | Very High | Growing | High | Varied | Rapidly Growing |
| Germany | High | Metals, Wood | Moderate | Strong | High | Strict | Wealthy |
| Japan | High | Limited | High | Moderate | High | Strict | Wealthy |
| Scandinavia | Moderate | Wood | Moderate | Strong | Moderate | Strict | Wealthy |
| Middle East | Varied | Limited | Very High | Emerging | Moderate | Varied | Varied |
| Australia | Moderate | Metals, Minerals | High | Strong | Moderate | Moderate | Wealthy |
| Silicon Valley (USA) | High | Limited | Moderate | Strong | Very High | Strict | Wealthy |
| Shenzhen (China) | High | Limited | High | Moderate | Very High | Varied | Rapidly Growing |
Key Insights:
- Industrial and Economic Development: In regions with significant industrial, construction, or manufacturing activities, such as the United States, China, Germany, and Japan, there is usually a high demand for various types of drill bits, especially those used in heavy machinery, construction, and manufacturing.
- Local Resources and Materials: The prevalence of certain materials (like wood in Scandinavia or metals in Australia) can influence the demand for specific types of drill bits. For instance, regions rich in wood resources might have higher sales of wood-specific drill bits.
- Construction Trends: In areas with booming construction industries, such as in some Middle Eastern countries or rapidly developing regions in Asia, there might be a higher demand for masonry and concrete drill bits.
- DIY Culture: In regions with a strong culture of DIY and home improvement, like in many parts of North America and Europe, there is likely to be a higher sale of general-purpose drill bits suitable for home use.
- Technological Advancements: Regions that are hubs of technological innovation (like Silicon Valley in the USA or Shenzhen in China) may see higher sales in specialized drill bits used in technology manufacturing and development.
- Regulatory Environment: The regulatory environment can also impact drill bit sales. For instance, regions with strict environmental regulations might see higher sales in eco-friendly or sustainable drilling solutions.
- Economic Factors: General economic conditions, such as a country’s GDP, disposable income levels, and industrial investment, can also influence drill bit sales. Wealthier countries might have higher overall sales due to more extensive industrial and construction activities and higher consumer spending in DIY and home improvement.
Innovation and Trends
The evolution of drill bit technology has been marked by significant advancements and innovations over the years, adapting to the changing needs of various industries. Here’s an overview of this evolution and some emerging trends in the market:
Evolution of Drill Bit Technology
| Era/Development | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Early Innovations | Flint/stone tools; later metal bits | Foundation of drilling technology |
| Twist Drill Bits (19th Century) | Invention by Stephen A. Morse | Revolutionized drilling efficiency |
| Carbide Drill Bits (20th Century) | Tungsten carbide bits for harder materials | Enhanced precision and speed |
| Diamond Drill Bits | Bits with embedded diamonds for hard materials | Enabled drilling in stone, glass, composites |
| Cobalt Drill Bits | Developed for extremely hard materials | Improved heat resistance and longevity |
Key Insights:
- Early Innovations: The earliest drill bits were simple tools made from flint or stone. With the advent of the Industrial Revolution, metal drill bits began to emerge.
- Twist Drill Bits: The invention of the twist drill bit in the 19th century by Stephen A. Morse was a significant milestone. These bits are still widely used today.
- Carbide Drill Bits: The development of tungsten carbide drill bits in the 20th century allowed for drilling through harder materials at faster speeds and with greater precision.
- Diamond Drill Bits: The introduction of diamond drill bits, using small diamonds embedded in the bit, allowed for cutting through very hard materials like stone, glass, and later, advanced composites.
- Cobalt Drill Bits: Cobalt drill bits emerged as a solution for drilling through extremely hard materials, offering heat resistance and extended longevity.
Emerging Trends in Drill Bit Market
| Trend | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Coatings and Materials | Use of titanium nitride, black oxide, etc. | Extended life and performance |
| Specialized Geometry | Design tailored to specific materials/applications | Improved efficiency in specialized tasks |
| Automation and Smart Tech | Automated changers, wear detection sensors | Precision in complex environments |
| Eco-Friendly Solutions | Sustainable manufacturing and materials | Addressing environmental concerns |
| Customization and 3D Printing | Custom-made bits for specific tasks | Enhanced versatility and specificity |
| Enhanced Cooling Techniques | Advanced cooling for high-speed applications | Prolonged life and efficiency |
| Multi-Functionality | Multi-purpose or multi-functional bits | Reduced need for multiple tools |
Key Insights:
- Coatings and Materials: Recent advancements include the use of various coatings (like titanium nitride, black oxide, diamond powder) to extend the life of drill bits and enhance their performance. New materials, such as polycrystalline diamond (PCD), are also being explored.
- Specialized Geometry: The design and geometry of drill bits are becoming more specialized to cater to specific materials and applications, such as aerospace composites or ultra-hard metals.
- Automation and Smart Technology: Integration of smart technologies for precision drilling in complex manufacturing environments, including automated drill bit changers and sensors for wear detection.
- Eco-Friendly Solutions: With growing environmental concerns, there is a trend towards more sustainable manufacturing processes and materials, including recyclable and biodegradable components.
- Customization and 3D Printing: Custom-made drill bits designed for specific applications are becoming more common, facilitated by technologies like 3D printing.
- Enhanced Cooling Techniques: Development of advanced cooling techniques to extend drill bit life and efficiency, especially in high-speed and high-friction applications.
- Multi-Functionality: The development of multi-purpose or multi-functional drill bits that can perform a variety of tasks with one tool, reducing the need for multiple bit changes.
This overview captures the general trends and historical progression in drill bit technology, reflecting the industry’s ongoing efforts to improve efficiency, precision, and material compatibility.
